 |
| Laue diagram of a crystal See: Experimental diffraction |
 |
| The Laue method in transmission mode |
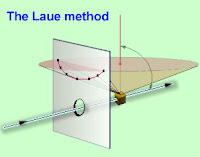 |
| The Laue method in reflection mode |
There are two different geometries in the Laue method, depending on the crystal position with regard to the photographic plate: transmission or reflection.
 |
Concerning the Detection of X-ray Interferences |
***
Max Theodor Felix von Laue (9 October 1879 – 24 April 1960) was a Germanphysicist who won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1914 for his discovery of the diffraction of X-rays by crystals. In addition to his scientific endeavors with contributions in optics, crystallography, quantum theory, superconductivity, and the theory of relativity, he had a number of administrative positions which advanced and guided German scientific research and development during four decades. A strong objector to National Socialism, he was instrumental in re-establishing and organizing German science after World War II.
| Max von Laue | |
|---|---|
Laue in 1929 |
Contents1 Biography |
See:
Also See:


No comments:
Post a Comment